How Virtual Sexual Experiences Could Help Reduce STD Rates in the United States
Introduction
The purpose of this study is to look at the correlation between rising STD rates in the United States and the widespread use of mobile apps and services which encourage people to meet in real life and how virtual sexual experiences online could contribute to reducing the STD rate across the country. In the study we use the latest STD statistics nationwide as provided by a publication from the CDC in October 2016 and look at the most popular dating apps used to meet in real life and the most popular virtual sexual experience services online.
STD Statistics in the United States
The following statistics are taken from national surveillance data for 2015, the latest data available, and cover the three notifiable diseases for which there are federally funded control programs – chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. As it is pertinent to this study, we have displayed the total number of cases, the rate of cases, the infection rate between sexes, and data on age groups for each disease below.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is the most common notifiable STD in the United States and has been among the most prevalent STDs, accounting for the largest proportion of all STDs since 1994. In 2015, a total of 1,526,658 chlamydia infections were reported in the United States, corresponding to a rate of 478.8 cases per 100,000 population.
The overall rate of chlamydia infections in the United States among women at 645.5 cases per 100,000 females is over twice that of men at 305.2 cases per 100,000 males. This data, however, reflects the larger number of women screened for the infection. The increased availability of urine testing for males is leading to a greater number of men, including gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men, being tested for chlamydia with the rate of the STD in males increasing by 20% between 2011-2015 compared with a 0.3% increase in women during the same period.
The rates of reported cases of chlamydia are highest among adolescents and young adults aged between 15 and 24 years old. The rates among 15 to 19 year olds was 1,857.8 per 100,000 population in 2015, and the rate among 20 to 25 year olds was 2,574.9 cases per 100,000 population. The highest age-specific rates of reported cases among females were for those aged between 15 and 19 and 20 and 24, while for males the highest age-specific rates were among those aged between 20 and 24.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported notifiable STD in the United States. In 2015, 395,216 gonorrhea cases were reported for a rate of 123.9 cases per 100,000 population in the country.
The overall rate of gonorrhea infections across the United States is higher in men at 140.9 cases per 100,000 males than it is for females at 107.2 cases per 100,000 females. There has been a significant increase in the rates of gonorrhea in males since 2011, with an increase of 44% being recorded during this period while the rate among females has dropped 0.7% during the same time. This may suggest either increased transmission of the disease or an increase in males, particularly gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men being screened.
In 2015, the rates of reported cases of gonorrhea is highest among adolescents and young adults. Persons aged between 15 and 44 account for 92.7% of all reported gonorrhea cases in 2015. Rates among females are the highest in those aged between 20 and 24 with 546.9 cases per 100,000 females, with the same age group also the highest for reported cases among males with 539.1 cases per 100,000 males and the 25 to 29 age group reporting 448.8 cases per 100,000 males in 2015.
Syphilis
Syphilis is associated with significant complications if left untreated and can facilitate the transmission and acquisition of HIV infections. It is the third most common STD infection in the United States with a total of 23,872 P&S (Primary and Secondary) syphilis cases reported representing a rate of 7.5 cases per 100,000 population.
The rate of P&S syphilis is significantly higher among men at 13.7 cases per 100,000 population than among women at 1.4 cases per 100,000 population. Males accounted for 90.3% of all reported syphilis cases in 2015, however, there was an increase of P&S syphilis cases reported among women by 27.3%. The majority of P&S syphilis cases reported are accounted for by gay, bisexual, and men who have sex with other men with 54% of the reported cases covering this category.
In 2015, reported cases of P&S syphilis were highest among persons aged between 24 and 29 and 20 and 24. The highest rates were observed for males between 25 and 29 with 41.8 cases per 100,000 and 20 to 24 with 35.7 cases per 100,000. These age group also accounted for the highest rates among females with 4.5 cases per 100,000 for females aged between 25 and 29 and 5.1 cases for females aged between 20 and 24.
STD Rates Since The Release of Popular Dating Apps
The rise in popularity of dating apps which make it easy to meet people in real life have strong correlations with recent rises in STD rates across the United States. Although it is impossible to attribute the rise in STDs to one cause such as the ease in which people can meet for casual sex due to apps such as Tinder and Grindr, there is evidence to support the theory that these apps are at least partially responsible. Below we will look at STD rates since the release of these two major dating apps to show how they have risen since these apps have become available.

Tinder
Tinder was released in 2012 and has since become one of the most popular dating apps in the world for both men and women. The app allows people to geo search other people and chat via the built in system as well as meet in real life. At present, an estimated 50 million people use Tinder worldwide, with 10 million active daily users, 14 billion swipes per day, and 26 million daily matches. Although advertised as a dating app, it is common knowledge that many people use Tinder as a hookup or casual sex app. The most prevalent age group on Tinder is 16 to 34, a group which coincides with the highest rates of all STDs mentioned in this study.
Each of the three STDs mentioned above have increased in prevalence since 2012, with all of them experiencing an extremely high rate in 2015 compared to previous years. In 2015 alone, rates of chlamydia have increased by 5.9% on 2014, rates of gonorrhea have increased by 12.8% on 2014, and rates of syphilis have increased by 19% on 2014. Although factors such as easier and more common testing could account for some of the increase in reported cases, apps such as Tinder which are used for casual sex certainly have had an impact on the consistent increase of STDs since its release.
Grindr
Grindr was releases in 2009, and has since become the largest and most popular male-based dating app on the market. Like Tinder, the app allows people to geo search other users, however, Grindr is designed for use by gay, bisexual, and other men who want to have sex with men. The app has over 6 million active users with 1.4 million users logging on daily around the world.
Men who have sex with men are at a higher risk of contracting a STD, specifically syphilis and rates for this group have increased at a faster rate between 2012 and 2015 than for men who have sex with women. In 2015, 81.7% of all syphilis cases reported were accounted for by this group.
Syphilis has been steadily increasing among men who have sex with men since 2012. In fact, the figure has risen by almost 50% since 2012, with 49% of the cases reported in 2015 also reported to be HIV-positive. These statistics correlate with the rise in popularity of apps such as Grindr which make it easy for men to meet other men for casual sex.
“ There is evidence to support the theory that these apps are at least partially responsible. ”
Alternatives to Geo Location and Real Life Meetup Apps
Due in part to the risks of contracting STDs from geo location services such as Tinder and Grindr, alternative services where users can enjoy a sexual experience without risk are growing in popularity. A recent study conducted by chat review site, Chatreviews, shows massive growth in the cam to cam random chat industry throughout 2016. This growth could be in part down to people worrying about engaging in real life casual sex and instead turning to safer means in order to meet new people.

The benefits of using such services go beyond simply eliminating the risks of contracting a STD. Users can also meet people from anywhere in the world instead of being restricted to only meeting people in close proximity. It also eliminates any danger of meeting a stranger in person, taking away all risks from real life meetups.
The evidence of people turning to such services can be visualized below with data from Alexa for Privr, a popular gay random chat site:
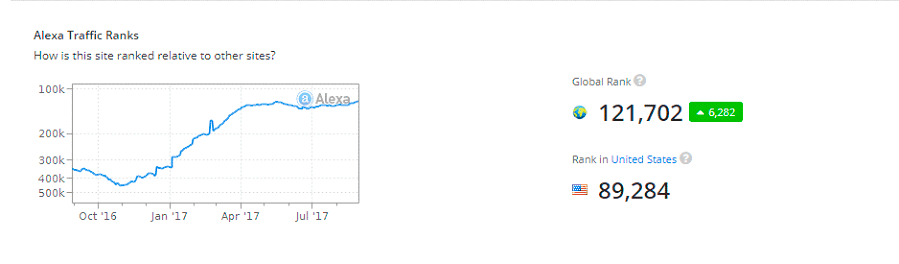
Conclusion
The data above shows a strong correlation between STD rates rising across the United States and the rise of apps such as Grindr and Tinder which allow geo based meetups and facilitate casual sex. Tackling the issue is extremely difficult, however, the increase in popularity of cam to cam services such as Privr may offer a partial solution. If people engage in virtual sex online rather than meeting in person, it is extremely likely that we will see a drop in the STD rates across the United States. If people change their sexual habits and use virtual sex over real life casual sex, it could dramatically decrease the number of reported STD cases in the near future.
